最近在搞编译优化和安全优化,话不多说,这里简单的笔记下使用记录吧,免得以后又忘了。
CONTENTS
strip
strip – Discard symbols from object files.
$ strip -h
用法:strip <选项> 输入文件
从文件中删除符号和节
选项为:
-I --input-target=<bfdname> Assume input file is in format <bfdname>
-O --output-target=<bfdname> Create an output file in format <bfdname>
-F --target=<bfdname> Set both input and output format to <bfdname>
-p --preserve-dates Copy modified/access timestamps to the output
-D --enable-deterministic-archives
Produce deterministic output when stripping archives (default)
-U --disable-deterministic-archives
Disable -D behavior
-R --remove-section=<name> Also remove section <name> from the output
--remove-relocations <name> Remove relocations from section <name>
-s --strip-all Remove all symbol and relocation information
-g -S -d --strip-debug Remove all debugging symbols & sections
--strip-dwo Remove all DWO sections
--strip-unneeded Remove all symbols not needed by relocations
--only-keep-debug Strip everything but the debug information
-M --merge-notes Remove redundant entries in note sections (default)
--no-merge-notes Do not attempt to remove redundant notes
-N --strip-symbol=<name> Do not copy symbol <name>
-K --keep-symbol=<name> Do not strip symbol <name>
--keep-file-symbols Do not strip file symbol(s)
-w --wildcard Permit wildcard in symbol comparison
-x --discard-all Remove all non-global symbols
-X --discard-locals Remove any compiler-generated symbols
-v --verbose List all object files modified
-V --version Display this program's version number
-h --help Display this output
--info List object formats & architectures supported
-o <file> Place stripped output into <file>
strip:支持的目标: elf64-x86-64 elf32-i386 elf32-iamcu elf32-x86-64 a.out-i386-linux pei-i386 pei-x86-64 elf64-l1om elf64-k1om elf64-little elf64-big elf32-little elf32-big pe-x86-64 pe-bigobj-x86-64 pe-i386 plugin srec symbolsrec verilog tekhex binary ihex
将 bug 报告到 <http://www.sourceware.org/bugzilla/>
nm
nm – list symbols from object files.
nm -h
用法:nm [选项] [文件]
列举 [文件] 中的符号 (默认为 a.out)。
The options are:
-a, --debug-syms Display debugger-only symbols
-A, --print-file-name Print name of the input file before every symbol
-B Same as --format=bsd
-C, --demangle[=STYLE] Decode low-level symbol names into user-level names
The STYLE, if specified, can be `auto' (the default),
`gnu', `lucid', `arm', `hp', `edg', `gnu-v3', `java'
or `gnat'
--no-demangle Do not demangle low-level symbol names
-D, --dynamic Display dynamic symbols instead of normal symbols
--defined-only Display only defined symbols
-e (ignored)
-f, --format=FORMAT Use the output format FORMAT. FORMAT can be `bsd',
`sysv' or `posix'. The default is `bsd'
-g, --extern-only Display only external symbols
-l, --line-numbers Use debugging information to find a filename and
line number for each symbol
-n, --numeric-sort Sort symbols numerically by address
-o Same as -A
-p, --no-sort Do not sort the symbols
-P, --portability Same as --format=posix
-r, --reverse-sort Reverse the sense of the sort
--plugin NAME Load the specified plugin
-S, --print-size Print size of defined symbols
-s, --print-armap Include index for symbols from archive members
--size-sort Sort symbols by size
--special-syms Include special symbols in the output
--synthetic Display synthetic symbols as well
-t, --radix=RADIX Use RADIX for printing symbol values
--target=BFDNAME Specify the target object format as BFDNAME
-u, --undefined-only Display only undefined symbols
--with-symbol-versions Display version strings after symbol names
-X 32_64 (ignored)
@FILE Read options from FILE
-h, --help Display this information
-V, --version Display this program's version number
nm:支持的目标: elf64-x86-64 elf32-i386 elf32-iamcu elf32-x86-64 a.out-i386-linux pei-i386 pei-x86-64 elf64-l1om elf64-k1om elf64-little elf64-big elf32-little elf32-big pe-x86-64 pe-bigobj-x86-64 pe-i386 plugin srec symbolsrec verilog tekhex binary ihex
将 bug 报告到 <http://www.sourceware.org/bugzilla/>。
readelf
readelf – Displays information about ELF files.
$ readelf -H
用法:readelf <选项> elf-文件
显示关于 ELF 格式文件内容的信息
Options are:
-a --all Equivalent to: -h -l -S -s -r -d -V -A -I
-h --file-header Display the ELF file header
-l --program-headers Display the program headers
--segments An alias for --program-headers
-S --section-headers Display the sections' header
--sections An alias for --section-headers
-g --section-groups Display the section groups
-t --section-details Display the section details
-e --headers Equivalent to: -h -l -S
-s --syms Display the symbol table
--symbols An alias for --syms
--dyn-syms Display the dynamic symbol table
-n --notes Display the core notes (if present)
-r --relocs Display the relocations (if present)
-u --unwind Display the unwind info (if present)
-d --dynamic Display the dynamic section (if present)
-V --version-info Display the version sections (if present)
-A --arch-specific Display architecture specific information (if any)
-c --archive-index Display the symbol/file index in an archive
-D --use-dynamic Use the dynamic section info when displaying symbols
-x --hex-dump=<number|name>
Dump the contents of section <number|name> as bytes
-p --string-dump=<number|name>
Dump the contents of section <number|name> as strings
-R --relocated-dump=<number|name>
Dump the contents of section <number|name> as relocated bytes
-z --decompress Decompress section before dumping it
-w[lLiaprmfFsoRtUuTgAckK] or
--debug-dump[=rawline,=decodedline,=info,=abbrev,=pubnames,=aranges,=macro,=frames,
=frames-interp,=str,=loc,=Ranges,=pubtypes,
=gdb_index,=trace_info,=trace_abbrev,=trace_aranges,
=addr,=cu_index,=links,=follow-links]
Display the contents of DWARF debug sections
--dwarf-depth=N Do not display DIEs at depth N or greater
--dwarf-start=N Display DIEs starting with N, at the same depth
or deeper
-I --histogram Display histogram of bucket list lengths
-W --wide Allow output width to exceed 80 characters
@<file> Read options from <file>
-H --help Display this information
-v --version Display the version number of readelf
将 bug 报告到 <http://www.sourceware.org/bugzilla/>
可以看出,strip是用来裁剪符号表的,nm和readelf是用来解析符号表的。这里具体分析下,首先建立几个对比文件,命令如下:
# 假定org是 -g 编译链接的一个可执行文件 # 对org进行分析 $ readelf -a -g -t --dyn-syms org > org.elf $ nm -l org > org.nm # 使用strip默认参数进行裁剪 $ cp org default_strip $ strip default_strip $ readelf -a -g -t --dyn-syms default_strip > default_strip.elf $ nm -l default_strip > default_strip.nm #使用strip -s进行裁剪 $ cp org strip_all $ strip -s strip_all $ readelf -a -g -t --dyn-syms strip_all > strip_all.elf $ nm strip_all > strip_all.nm #使用strip -g进行裁剪 $ cp org strip_dbg $ strip -g strip_dbg $ readelf -a -g -t --dyn-syms strip_dbg > strip_dbg.elf $ nm strip_dbg > strip_dbg.nm #使用strip -x进行裁剪 $ cp org strip_x $ strip -x strip_x $ nm strip_x > strip_x.nm $ readelf -a -g -t --dyn-syms strip_x > strip_x.elf #使用strip -X进行裁剪 $ cp org strip_X $ readelf -a -g -t --dyn-syms strip_X > strip_X.elf $ nm strip_X > strip_X.nm $ ls -l #打印文件类型 $ file org org: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/l, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, BuildID[sha1]=972680aa8cffbf12e21466a284eb6141d334ea12, with debug_info, not stripped $ file default_strip default_strip: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/l, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, BuildID[sha1]=972680aa8cffbf12e21466a284eb6141d334ea12, stripped $ file strip_all strip_all: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/l, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, BuildID[sha1]=972680aa8cffbf12e21466a284eb6141d334ea12, stripped $ file strip_dbg strip_dbg: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/l, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, BuildID[sha1]=972680aa8cffbf12e21466a284eb6141d334ea12, not stripped $ file strip_x strip_x: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/l, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, BuildID[sha1]=972680aa8cffbf12e21466a284eb6141d334ea12, not stripped $ file strip_X strip_X: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/l, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, BuildID[sha1]=972680aa8cffbf12e21466a284eb6141d334ea12, with debug_info, not stripped #打印文件大小 $ ls -l 总用量 90676 -rwxr-xr-x 1 cstriker1407 cstriker1407 837160 1月 2 17:28 default_strip -rw-r--r-- 1 cstriker1407 cstriker1407 58808 1月 2 17:28 default_strip.elf -rw-r--r-- 1 cstriker1407 cstriker1407 0 1月 2 17:37 default_strip.nm -rwxr-xr-x 1 cstriker1407 cstriker1407 1626272 1月 2 17:13 org -rw-r--r-- 1 cstriker1407 cstriker1407 265352 1月 2 17:26 org.elf -rw-r--r-- 1 cstriker1407 cstriker1407 276422 1月 2 17:27 org.nm -rwxr-xr-x 1 cstriker1407 cstriker1407 837160 1月 2 17:39 strip_all -rw-r--r-- 1 cstriker1407 cstriker1407 58808 1月 2 17:39 strip_all.elf -rw-r--r-- 1 cstriker1407 cstriker1407 0 1月 2 17:39 strip_all.nm -rwxr-xr-x 1 cstriker1407 cstriker1407 945880 1月 2 17:40 strip_dbg -rw-r--r-- 1 cstriker1407 cstriker1407 257265 1月 2 17:40 strip_dbg.elf -rw-r--r-- 1 cstriker1407 cstriker1407 97071 1月 2 17:40 strip_dbg.nm -rwxr-xr-x 1 cstriker1407 cstriker1407 899688 1月 2 17:40 strip_x -rw-r--r-- 1 cstriker1407 cstriker1407 171052 1月 2 17:41 strip_x.elf -rw-r--r-- 1 cstriker1407 cstriker1407 52920 1月 2 17:41 strip_x.nm -rwxr-xr-x 1 cstriker1407 cstriker1407 1626272 1月 2 17:41 strip_X -rw-r--r-- 1 cstriker1407 cstriker1407 265352 1月 2 17:41 strip_X.elf -rw-r--r-- 1 cstriker1407 cstriker1407 97071 1月 2 17:41 strip_X.nm
下面来详细分析下。
strip -s VS strip
通过文件大小和二进制对比,可以看出两个是一致的。因此可以认为strip默认选项即为 strip -s。
org VS strip-s
对比下elf文件,我们可以发现,strip -s 才减掉了debug*,symtab和strtab,由于将symtab全部才裁剪掉了,因此nm也没有输出。
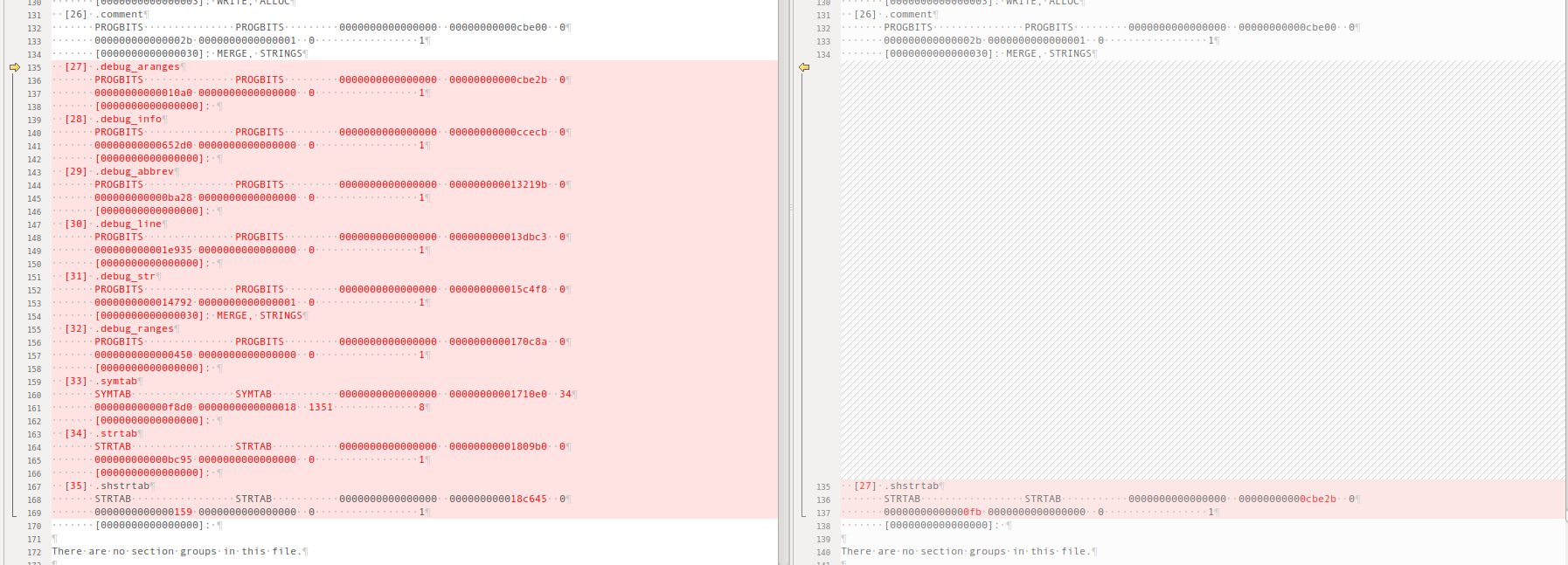
org VS strip -g
对比下elf文件,我们可以发现,strip -g 才减掉了debug*,symtab,strtab还存在,因此因此nm还是有输出的。但是对比nm输出文件可以看到,函数位置已经没有了。
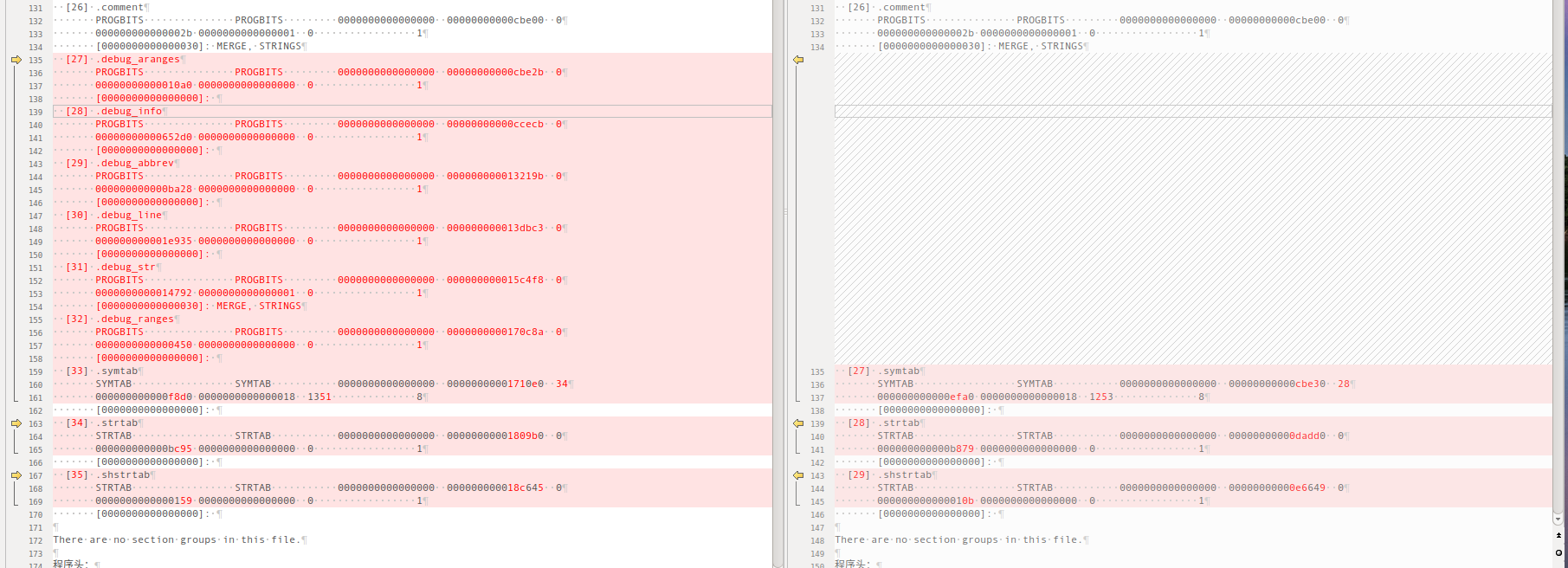
org VS strip -x
对比下elf文件,我们可以发现,strip -x 才减掉了debug*,symtab进行了大量删减,只保留了很少一部分内容,因此还是有nm输出。
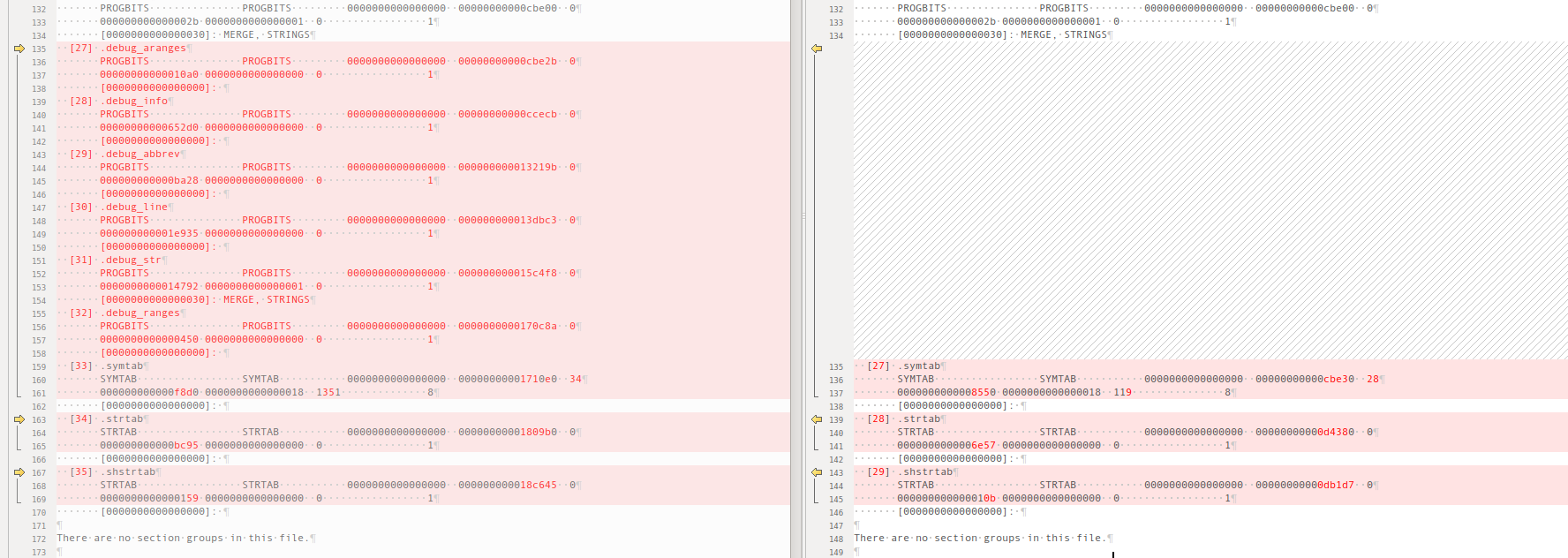
 org VS strip -X
org VS strip -X
作者测试发现没有任何变动,就暂时不深究了。
cutter安全分析
我们使用strip对输出文件进行裁剪不仅仅是为了减小文件大小,还有一个很重要的原因是安全考虑。这里我们使用cutter对几个输出进行简单的分析,看下各个文件反汇编和定位核心函数的成本。
org
org包含了debug*,symtab,strtab,对org文件进行分析,可以非常直观的看到各个函数的名称,所在的符号表等,如下图所示:
通过函数搜索,就可以很容易的找到核心函数,然后尝试反编译,如下图:
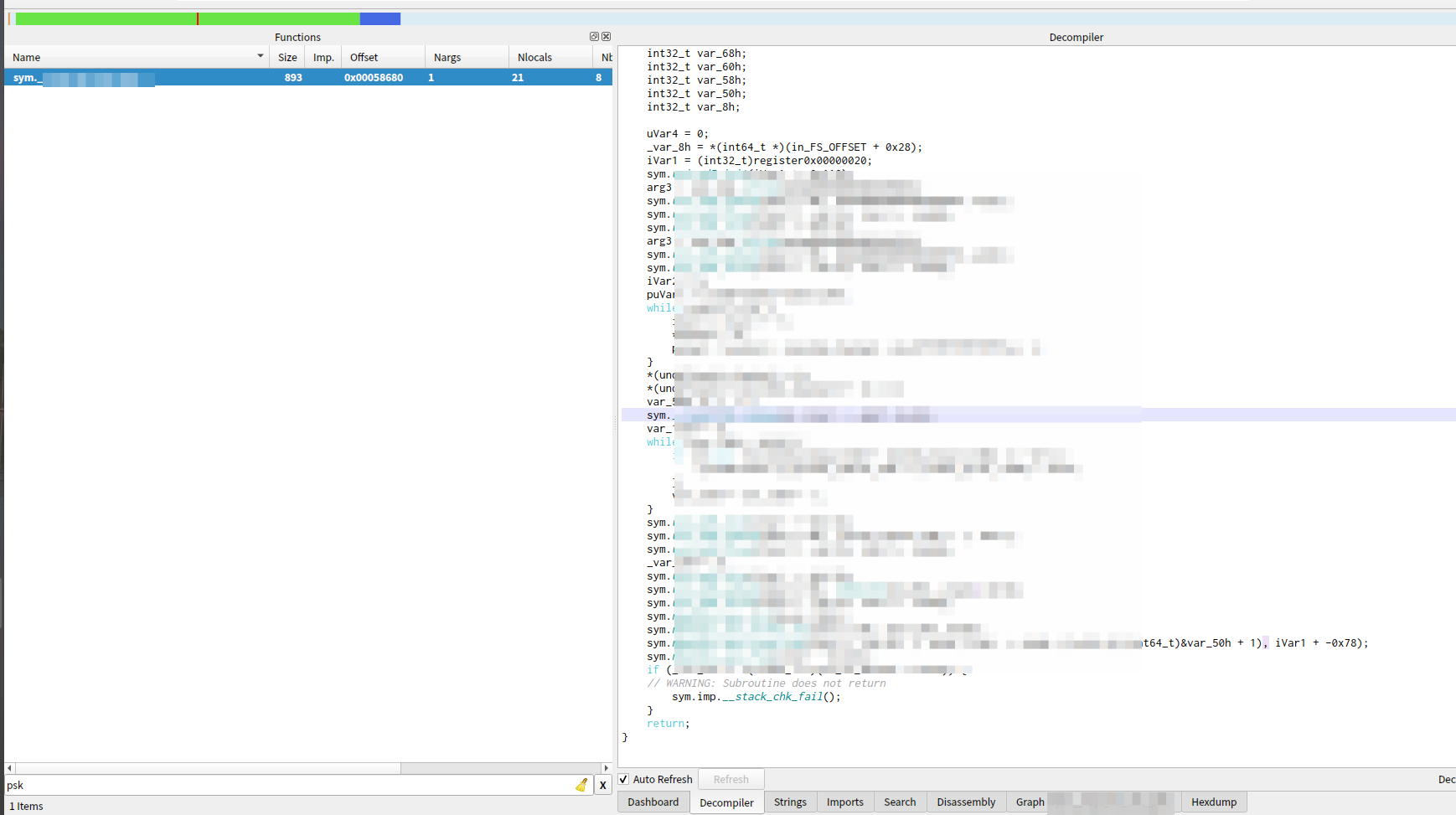
可以看到,可以非常容易的看到函数执行流程,在汇编TAB页甚至可以看到函数所在的源文件的位置。
strip_dbg
strip_dbg去掉了debug*,包含了symtab,strtab,对strip_dbg文件进行分析,可以非常直观的看到各个函数的名称,所在的符号表等,如下图所示:
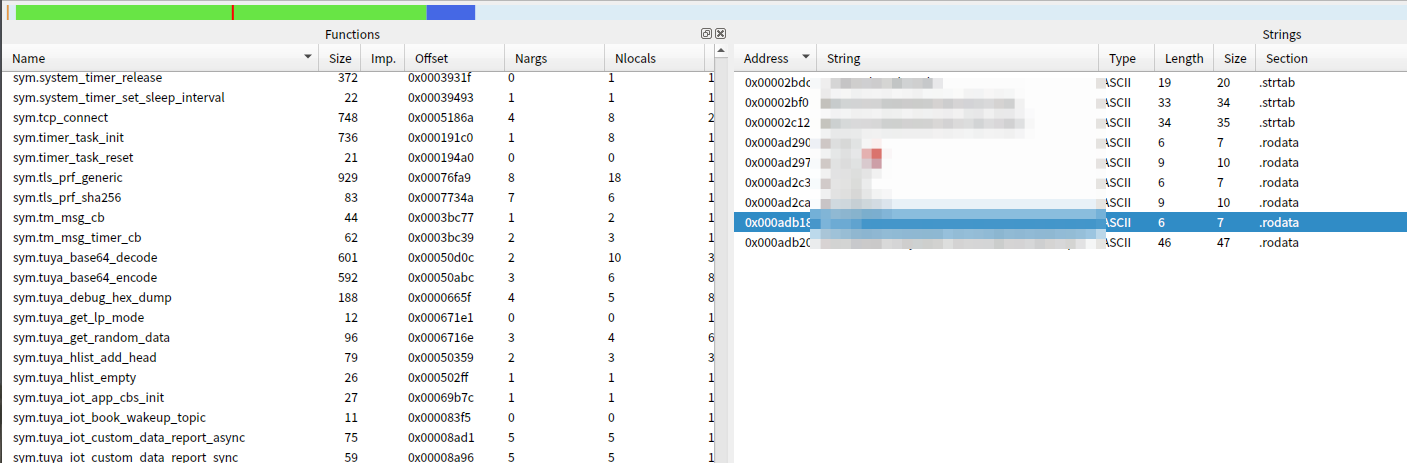
由于symtab存在,我们也可以很容易的通过函数搜索来定位到核心函数,进而看到函数执行流程。
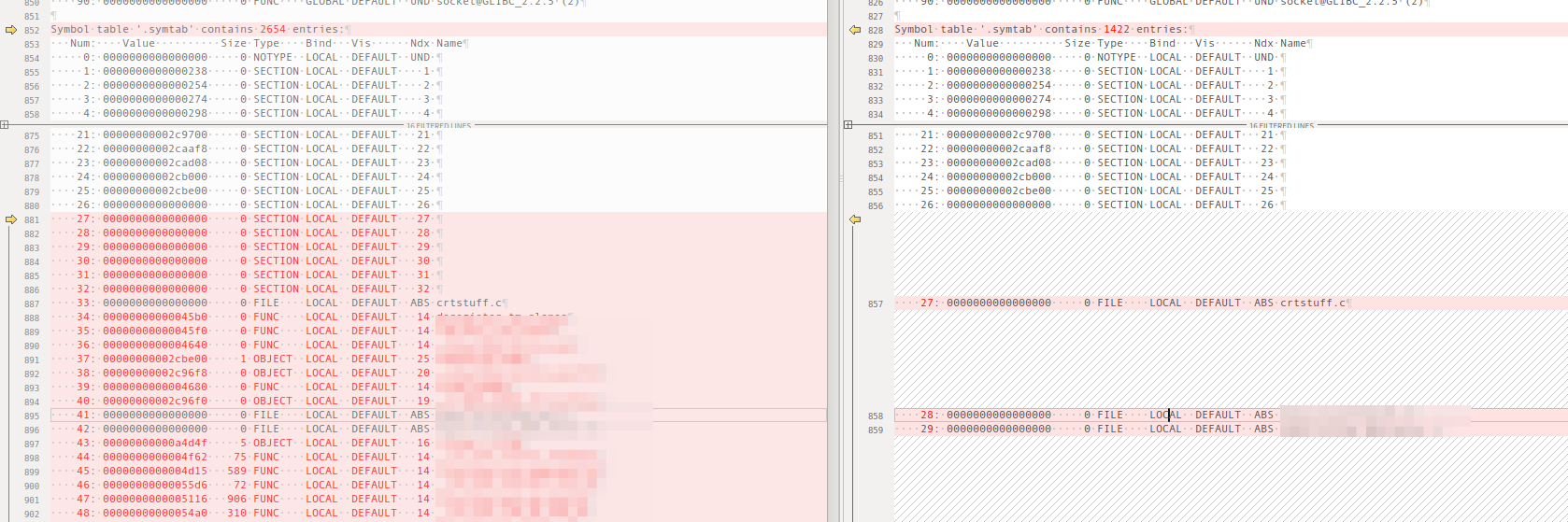
strip_all
strip_all去掉了debug*,symtab,strtab,对strip_all文件进行分析,如下图所示:
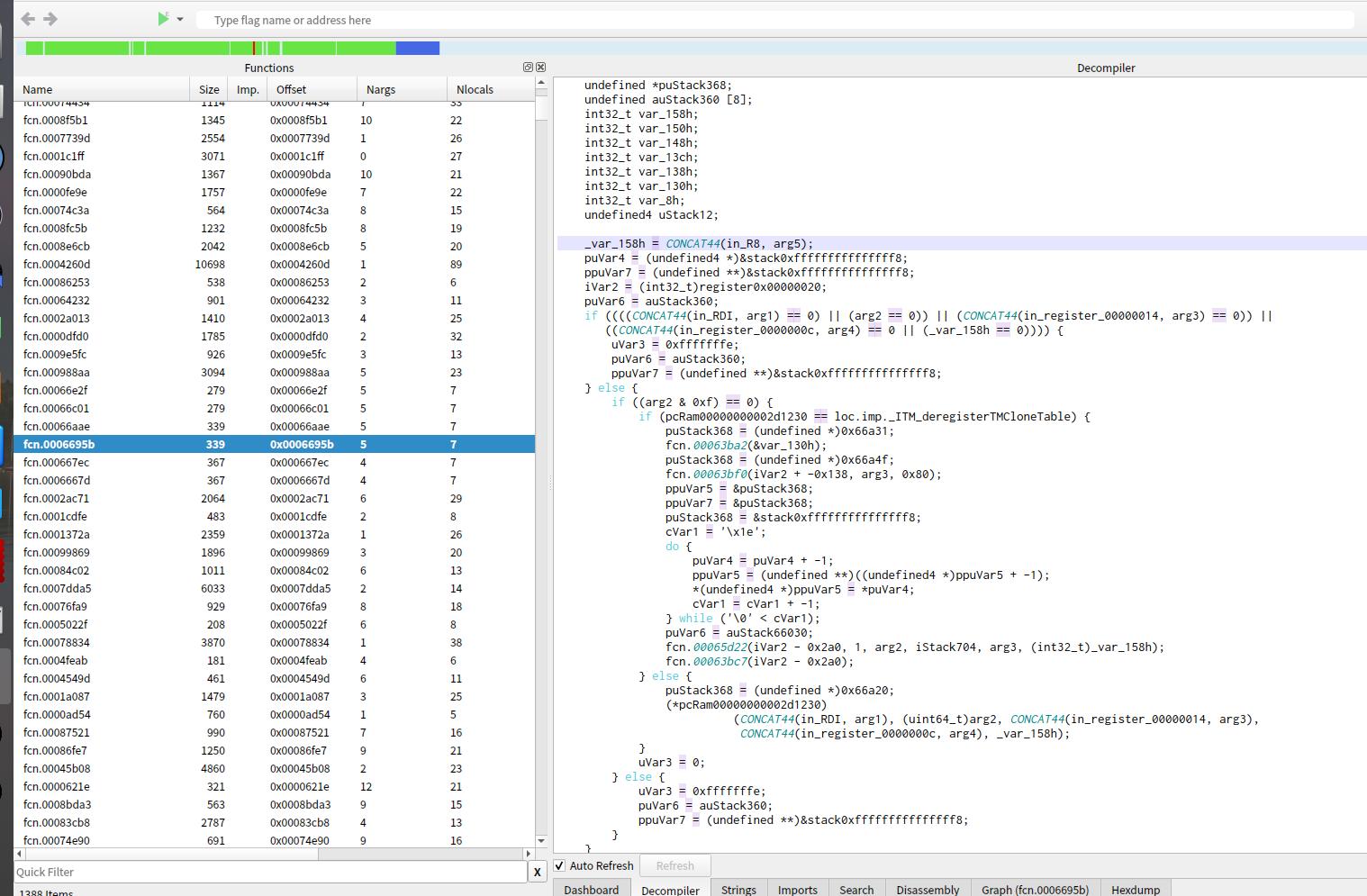
可以看到,虽然函数流程依然被反汇编了,但是由于symtab被裁剪,反汇编后的函数可读性已经非常差了,定位核心函数就会变得比较困难。
综上,考虑到和文件大小和安全,作者这里建议使用strip默认参数,也就是strip -s,将debug*和symtab全部裁剪掉。
发表评论